作者:叶金荣 转载至:http://imysql.com/2013/08/15/innodb-memcached-vs-native-memcached-benchmark.shtml
MySQL 5.6开始支持InnoDB memcached插件,也就是可以通过SQL高效读写memcached里的缓存内容,也支持用原生的memcache协议读写,并且可以实现缓存数据持久化,以及crash recovery、mysql replication、触发器、存储过程等众多特性,详细介绍可以查看:Benefits of the InnoDB / memcached Combination。看起来非常诱人,那就测试下看看吧,是驴子是马拉出来溜溜便知。
- 环境准备
| 测试机 | DELL PE R710 |
| CPU | E5620 @ 2.40GHz(4 core, 8 threads, L3 Cache 12 MB) * 2 |
| 内存 | 48G(8G * 6) |
| RAID卡 | PERC H700 Integrated, 512MB, BBU, 12.10.1-0001 |
| 系统 | Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.4 (Santiago) |
| 内核 | 2.6.32-358.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP |
| raid级别 | raid 5(10K RPM SAS 300G * 6) |
| 文件系统 | xfs |
| 硬盘 | 10K RPM SAS 300G * 6, 1 hotspare |
- 测试方案
| 方案一 | server端运行InnoDB MC,本地/远程调用memslap执行benchmark |
| 方案二 | server端运行Native MC,本地/远程调用memslap执行benchmark |
- 测试脚本
cat memslap_run.sh
#!/bin/sh
. ~/.bash_profile > /dev/null 2>&1
cd /home/mc-bench
exec 3>&1 4>&2 1>> memcache_memslap_${RANDOM}.log 2>&1
#不断循环
while [ 1 ]
do
#并发线程数 4 ~ 256
for THREAD in 4 8 16 32 64 128 256
do
#每种并发测试5次
count=1
max=5
while [ $count -le ${max} ]
do
#取样
echo "memstat"
memstat
# --flush 每次测试完毕钱,都先清空数据
# --binary 采用binary模式
# 初始化数据: 5000000, 每个并发线程存取数据量: 100000
# 并发256线程时, 总数据量可达 30,600,000
# 未指定 --test 选项,默认是进行 set 测试
memslap --server=mc_server:11211 --concurrency=${THREAD} --execute-number=100000 --initial-load=5000000 --flush --binary
count=`expr ${count} + 1`
#每次测试完毕后,都休息2分钟,等待服务器恢复空负载
if [ ${count} -lt ${max} ] ; then
sleep 120
fi
echo ""
echo ""
done
done
done
- 测试结果
1. 写MC
| 线程数 耗时 |
256 | 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 |
| NativeMC(单位:1秒) | 104.315 | 47.646 | 24.486 | 12.162 | 6.351 | 5.525 | 5.078 |
| InnoDBMC(单位:100秒) | 339.1431 | 68.11128 | 27.67265 | 11.26917 | 4.968556 | 2.24988 | 1.104334 |
直接以曲线图方式对比:
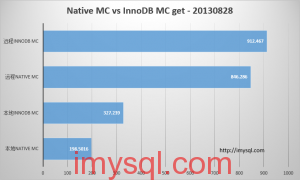
2. 读MC
| 线程数 耗时 |
4线程并发,2千万记录 |
| 本地Native MC | 198.5016 |
| 本地InnoDB MC | 327.239 |
| 远程Native MC | 846.286 |
| 远程InnoDB MC | 912.467 |
曲线图方式对比:
- 结论
InnoDB MC看起来很美好,现实很骨感,其并发4线程写数据需呀的耗时,和原生memcached的256线程相当,差的不是一丁半点啊,还有很大优化空间。
而如果是缓存只读,InnoDB MC本地读取的效率大概是原生memcached的2/3,如果是远程读取,则相当于是本地读取效率的1/4 ~ 1/3。
- 建议应用场景
鉴于上面的测试结果,建议将InnoDB MC这么来用:
1. 数据写入通过触发器(trigger)或者调度器(event scheduler)将待缓存数据同步到InnoDB MC缓存表中;
2. 以memcache API方式,通过本地/远程读取InnoDB MC中的缓存记录;
3. 尽可能减少通过远程方式往InnoDB MC写缓存数据;
 同乐学堂
同乐学堂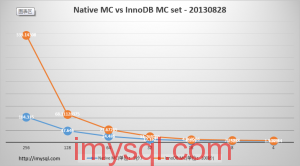

 微信扫一扫,打赏作者吧~
微信扫一扫,打赏作者吧~

